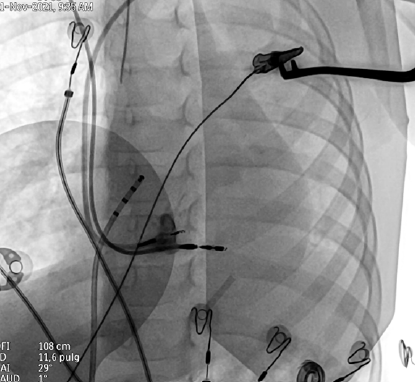
Left bundle branch stimulation in diffuse electrical heart disease in a pediatric patient
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47487/apcyccv.v3i4.239Keywords:
Bundle of His, Cardiac Pacing, Artificial, Cardiac Arhythmia, Sinus Node Dysfunction, PediatricsAbstract
Left bundle branch stimulation is a second-line strategy in patients where His bundle stimulation is not optimal. Currently, no cases of left bundle branch stimulation have been reported in patients with diffuse electrical cardiac disease or in the pediatric population.
Downloads
References
HuangW,SuL,WuS,XuL,XiaoF,ZhouX,etal.Anovelpacing strategy with low and stable output: pacing the left bundle branch immediately beyond the conduction block. Can J Cardiol. 2017;33(12):1736.e1-1736.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.09.013.
Li X, Li H, Ma W, Ning X, Liang E, Pang K, et al. Permanent left bundle branch area pacing for atrioventricular block: Feasibility, safety, and acute effect. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16(12):1766-1773. doi: 10.1016/j. hrthm.2019.04.043.
Iturralde-Torres P, Nava-Townsend S, Gómez-Flores J, Medeiros- Domingo A, Colín-Lizalde L, Hermosillo AG, et al. Association of congenital, diffuse electrical disease in children with normal heart: sick sinus syndrome, intraventricular conduction block, and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008;19(5):550-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.01006.x.
Kawata H, Pretorius V, Phan H, Mulpuru S, Gadiyaram V, Patel J, et al. Utility and safety of temporary pacing using active fixation leads and externalized re-usable permanent pacemakers after lead extraction. Europace. 2013;15(9):1287-91. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut045.
Lyon S, Dandamudi G, Kean A. Permanent His-bundle Pacing in Pediatrics and Congenital Heart Disease. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. 2020;11(2):4005-4012. doi: 10.19102/icrm.2020.110205.
Ponnusamy SS, Muthu G, Bopanna D. Selective left bundle branch pacing for pediatric complete heart block. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2020;20(2):78-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2019.12.012.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The journal is headline of the first publication, then the author giving credit to the first publication.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














