The role of agitated saline contrast echocardiography in the evaluation of pulmonary hypertension
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47487/apcyccv.v6i2.486Keywords:
Contrast Echocardiography, Echocardiography, Pulmonary Hypertension, Heart Septal Defects, AtrialAbstract
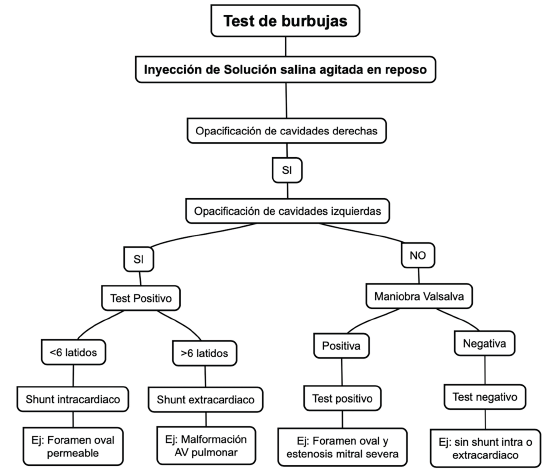
The diagnostic approach to pulmonary hypertension using cardiac imaging, particularly echocardiography, provides a practical, accessible, and highly valuable tool. It helps establish the initial diagnostic probability, offers prognostic information, and supports aetiological assessment. The agitated saline contrast test, also referred to as bubble contrast echocardiography, can aid not only in confirming the diagnosis but also in characterising the condition and identifying various underlying causes of pulmonary hypertension.
Downloads
References
Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(38):3618-731. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237.
Farber HW, Foreman AJ, Miller DP, McGoon MD. REVEAL Registry: Correlation of Right Heart Catheterization and Echocardiography in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: right heart catheterization vs echocardiography in PAH. Congest Heart Fail. 2011;17(2):56-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7133.2010.00202.x.
Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, Hua L, Handschumacher MD, Chandrasekaran K, et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23(7):685-713. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2010.05.010.
Cordina RL, Playford D, Lang I, Celermajer DS. State-of-the-Art Review: Echocardiography in Pulmonary Hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2019;28(9):1351-64. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2019.03.003.
Waggoner AD, Ehler D, Adams D, Moos S, Rosenbloom J, Gresser C, et al. Guidelines for the cardiac sonographer in the performance of contrast echocardiography: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council on Cardiac Sonography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2001;14(5):417-20. doi: 10.1067/mje.2001.113817.
Porter TR, Abdelmoneim S, Belcik JT, McCulloch ML, Mulvagh SL, Olson JJ, et al. Guidelines for the Cardiac Sonographer in the Performance of Contrast Echocardiography: A Focused Update from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(8):797-810. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.05.011.
Mattioli A. Atrial septal aneurysm as a cardioembolic source in adult patients with stroke and normal carotid arteries. A multicentre study. Eur Heart J. 2001;22(3):261-8. oi: 10.1053/euhj.2001.2293.
Natanzon A, Goldman ME. Patent foramen ovale: Anatomy versus pathophysiology—which determines stroke risk? J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16(1):71-6. doi: 10.1067/mje.2003.34.
Marriott K, Manins V, Forshaw A, Wright J, Pascoe R. Detection of Right-to-Left Atrial Communication Using Agitated Saline Contrast Imaging: Experience with 1162 Patients and Recommendations for Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013;26(1):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2012.09.007.
Silvestry FE, Cohen MS, Armsby LB, Burkule NJ, Fleishman CE, Hijazi ZM, et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect and Patent Foramen Ovale: From the American Society of Echocardiography and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(8):910-58. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.05.015.
Soliman O, Geleijnse M, Meijboom F, Nemes A, Kamp O, Nihoyannopoulos P, et al. The use of contrast echocardiography for the detection of cardiac shunts. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2007;8(3):S2-12. doi: 10.1016/j.euje.2007.03.006.
Sharan L, Stackhouse K, Awerbach JD, Bashore TM, Krasuski RA. Effect of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(3):505-10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.04.014.
Nootens MX, Berarducci LA, Kaufmann E, Devries S, Rich S. The Prevalence and Significance of a Patent Foramen Ovale in Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest. 1993;104(6):1673-5. doi: 10.1378/ chest.104.6.1673.
Bernard S, Churchill TW, Namasivayam M, Bertrand PB. Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography in the Identification of Intra- and Extracardiac Shunts: Connecting the Dots. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2021;34(1):1-12.
Romero JR, Frey JL, Schwamm LH, Demaerschalk BM, Chaliki HP, Parikh G, et al. Cerebral Ischemic Events Associated With ‘Bubble Study’ for Identification of Right to Left Shunts. Stroke. 2009;40(7):2343-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.549683.
Jeon DS, Luo H, Iwami T, Miyamoto T, Brasch AV, Mirocha J, et al. The usefulness of a 10% air-10% blood-80% saline mixture for contrast echocardiography: Doppler measurement of pulmonary artery systolic pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(1):124-9. doi: 10.1016/ s0735-1097(01)01698-9.
Attaran RR, Ata I, Kudithipudi V, Foster L, Sorrell VL. Protocol for Optimal Detection and Exclusion of a Patent Foramen Ovale Using Transthoracic Echocardiography with Agitated Saline Microbubbles. Echocardiography. 2006;23(7):616-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1540- 8175.2006.00272.x.
Wei D, Ju Y. Importance of an Adequately Performed Valsalva Maneuver for Detecting a Right‐to‐Left Shunt Indicating Foramen Ovale Reopening. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34(5):879-83. doi: 10.7863/ ultra.34.5.879.
Montrief T, Alerhand S, Denault A, Scott J. Point-of-care echocardiography for the evaluation of right-to-left cardiopulmonary shunts: a narrative review. Can J Anesth Can Anesth. 2020;67(12):1824- 38. doi: 10.1007/s12630-020-01813-2.
Freeman JA, Woods TD. Use of Saline Contrast Echo Timing to Distinguish Intracardiac and Extracardiac Shunts: Failure of the 3‐ to 5‐Beat Rule. Echocardiography. 2008;25(10):1127-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2008.00741.x.
Deri A, English K. Echocardiographic assessment of left to right shunts: atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, patent arterial duct. Echo Res Pract. 2018;5(1):R1-16. doi: 10.1530/ERP-17-0062.
Rasalingam R, Novak E, Rifkin RD. Improved differential diagnosis of intracardiac and extracardiac shunts using acoustic intensity mapping of saline contrast studies. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;21(3):307-317. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez129.
Yang J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Yu H, Zhang H, Lan T, et al. The efficiency of a Machine learning approach based on Spatio-Temporal information in the detection of patent foramen ovale from contrast transthoracic echocardiography Images: A primary study. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023;84:104813. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104813.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The journal is headline of the first publication, then the author giving credit to the first publication.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














