Acute cardiovascular complications in a Peruvian population of oncology patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47487/apcyccv.v3i1.192Keywords:
Neoplasms, Risk factors, Heart disease, Case reportsAbstract
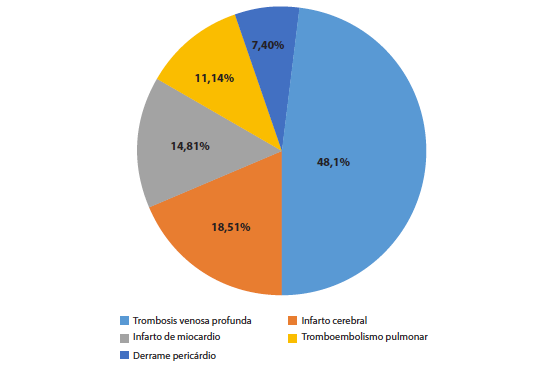
Objective. To know the most frequent acute cardiovascular complications in a Peruvian population of oncologic patients. Materials and methods. Retrospective, descriptive study of oncologic patients treated at Clinica Delgado between January 2014 and December 2019, from which the subgroup with the seven most prevalent cancers at the national level was selected according to information from Globocan 2018. Additionally, we evaluated the epidemiology of patients with cardiovascular complications that conditioned their hospitalization or were detected during this, calculating their cardiovascular risk according to Hermann and SCORE risk scales. Results. Forty-four patients had complications; 27 (61.4%) were hospitalized due to acute cardiovascular causes. The mean age of this subgroup was 69.88 years (SD 12.77), and 22 (81.5%) were older than 60 years. Fourteen (51.9%) were male. According to the Hermann scale, 33.3% had intermediaterisk and 14.9% had a high or very high risk. According to the SCORE scale, 62.97% had an intermediate-risk and 7.40% high risk. The most common acute cardiovascular complications were deep vein thrombosis and ischemic stroke (66.65%). One patient (3.7%) reported previous cardiovascular disease. Four patients (14.8%) had a fatal outcome during hospitalization. The median length of hospitalization was five days. Conclusions. We present the cases of acute cardiovascular complications in a population of oncologic patients and their vascular risk according to Hermann and SCORE scales. The most common complications were deep vein thrombosis (48.14%), stroke (18.51%), and myocardial infarction (14.81%).
Downloads
References
Aleman BMP, Moser EC, Nuver J, Suter TM, Maraldo MV, Specht L, et al. Cardiovascular disease after cancer therapy. EJC Suppl. 2014;12(1):18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcsup.2014.03.002.
Truong J, Yan AT, Cramarossa G, Chan KK. Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: detection, prevention, and management. Can J Cardiol. 2014;30(8):869-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2014.04.029.
Herrmann J, Lerman A, Sandhu NP, Villarraga HR, Mulvagh SL, Kohli M. Evaluation and management of patients with heart disease and cancer: cardio-oncology. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89(9):1287-306. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.05.013.
Garcia AM, Mitroi C, Mazon-Ramos P, Garcia -Sanz R, Virizuela JA, Arenas M, et al. Stratification and management of cardiovascular risk in cancer patients. A consensus document of the SEC, FEC, SEOM, SEOR, SEHH, SEMG, AEEMT, AEEC and AECC. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2021;74(5):438-448. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2020.11.020.
Bellinger AM, Arteaga CL, Force T, Humphreys BD, Demetri GD, Druker BJ, et al. Cardio-Oncology: How New Targeted Cancer Therapies and Precision Medicine Can Inform Cardiovascular Discovery. Circulation. 2015;132(23):2248-2258. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.010484.
Koutsoukis A, Ntalianis A, Repasos E, Kastritis E, Dimopoulos MA, Paraskevaidis I. Cardio-oncology: A Focus on Cardiotoxicity. Eur Cardiol. 2018;13(1):64-69. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2017:17:2.
Campia U, Moslehi JJ, Amiri-Kordestani L, Barac A, Beckman JA, Chism DD, et al. Cardio-Oncology: Vascular and Metabolic Perspectives. Circulation. 2019;139(13):e579-e602. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000641.
Totzeck M, Schuler M, Stuschke M, Heusch G, Rassaf T. Cardio-oncology - strategies for management of cancer-therapy related cardiovascular disease. Int J Cardiol. 2019;280:163-175. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.01.038.
31. Valenzuela-Rodríguez G, Pacheco-Mendoza M, Mezones-Holguín E. Actualización en Cardio-Oncología para el médico oncólogo clínico. Carcinos. 2016;6(2):81-90.
Tocchetti CG, Ameri P, De Boer RA, D´Alessandra YD, Russo M, Sorriento D. Cardiac dysfunction in cancer patients. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(11):1820-1834. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa222.
Suter TM, Ewer MS. Cancer drugs and the heart: importance and management. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(15):1102-11. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs181.
Akolkar G, Bhullar N, Bews H, Shaikh B, Premecz S, Bordun KA, et al. The role of renin angiotensin system antagonists in the prevention of doxorubicin and trastuzumab induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015;13:18. doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0011-x.
Lenneman CG, Sawyer DB. Cardio-Oncology: An Update on Cardiotoxicity of Cancer-Related Treatment. Circ Res. 2016;118(6):1008-1020. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303633.
Magnano LC, Martínez Cibrian N, Andrade González X, Bosch X. Cardiac complications of chemotherapy: role of prevention. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2014;16(6):312. doi: 10.1007/s11936-014-0312-7.
Asnani A. Cardiotoxicity of Immunotherapy: Incidence, Diagnosis, and Management. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018;20(6):44. doi: 10.1007/s11912-018-0690-1.
Coumbe BGT, Groarke JD. Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction in Patients with Cancer. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018;20(8):69. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-1010-y.
Tamargo J, Caballero R, Delpón E. Cancer Chemotherapy and Cardiac Arrythmias: a Review. Drug Saf. 2015;38(2):129-152. doi: 10.1007/s40264-014-0258-4.
Gevaert SA, Halvorsen S, Sinnaeve PR, Sambola A, Gulati G, Lancellotti P, et al. Evaluation and management of cancer patients presenting with acute cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2021;10(8):947-959. doi: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuab056.
Ruiz-Mori E, Ayala-Bustamante L, Burgos-Bustamante J, Pacheco-Román C. Cardiotoxicidad por quimioterapia en el Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplásicas 2012-2016. Horiz Med. 2017;17(3):24-28.
Salinas-Arce J, Valenzuela G, Gonzales A, Salinas E, Granados M. Disfunción severa del nodo sinusal inducida por un inhibidor de la tirosina quinasa. Carcinos. 2019;9(1):14-17.
De Wall C, Bauersachs J, Berliner D. Cardiooncology-dealing with modern drug treatment long-term complications, and cancer survivorship. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2021;38(4):361-371. doi: 10.1007/s10585-021-10106-x.
Lyon AR, Dent S, Stanway S , Earl H, Brezden-Masley C, Cohen-Solal A, et al. Baseline cardiovascular risk assessment in cancer patients scheduled to receive cardiotoxic cancer therapies: a position statement and new risk assessment tools from the Cardio-Oncology Study Group of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology in collaboration with the International Cardio-Oncology Society. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(11):1945-1960. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1920.
Peretto G, Lazzeroni D, Sartorio CL, Camici PG. Cardiotoxicity in oncology and coronary microcirculation: future challenges in theranostics. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017;22(10):1760-1773. doi: 10.2741/4570.
Graffagnino J, Kondapalli L, Arora G, Hawi R, Lenneman CG. Strategies to Prevent Cardiotoxicity. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020;21(4):32. doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-0722-6.
Seraphim A, Westwood M, Bhuva AN, Crake T, Moon JC, Menezes LJ, et al. Advanced Imaging Modalities to Monitor for Cardiotoxicity. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20(9):73. doi: 10.1007/s11864-019-0672-z.
Thavendiranathan P, Negishi T, Somerset E, Negishi K, Penicka M, Lemieux J, et al. Strain-Guided Management of Potentially Cardiotoxic Cancer Therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(4):392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.020.
Hamo CE, Bloom MW, Cardinale D, Ky B, Nohria A, Baer L, et al. Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction and Heart Failure: Part 2: Prevention, Treatment, Guidelines, and Future Directions. Circ Heart Fail. 2016;9(2):e002843. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.115.002843.
Pavo N, Raderer M, Hülsmann M, Neuhold S, Adlbrecht C, Strunk G, et al. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cancer and their association with all-cause mortality. Heart. 2015;101(23):1874-1880. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2015-307848.
Paredes-Paucar C, López-Fernández T. Rol del cardiólogo en el manejo de pacientes oncológicos. ¿Dónde estamos y a dónde debemos ir? Arch Peru Cardiol Cir Cardiovasc. 2021;2(2):103-111. doi: 10.47487/apcyccv.v2i2.140.
Moudgil R, Yeh ET. Mechanisms of Cardiotoxicity of Cancer Chemotherapeutic Agents: Cardiomyopathy and Beyond. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(7):863-870.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2016.01.027.
Shum K, Solivan A, Parto P, Polin N, Jahangir E. Cardiovascular Risk and Level of Statin Use Among Women With Breast Cancer in a Cardio-Oncology Clinic. Ochsner J. 2016;16(3):217-224.
Lagethon-Heck S, Mecinaj A, Hansen-Ree A , Hoffmann P, Schulz-Menger J, Wang-Ferland M, et al. Prevention of Cardiac Dysfunction During Adjuvant Breast Cancer Therapy (PRADA): Extended Follow-Up of a 2x2 Factorial, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trial of Candesartan and Metoprolol. Circulation. 2021;143(25):2431-2440. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.054698.