El rol del ecocardiograma de contraste con solución salina agitada en el abordaje de la hipertensión pulmonar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47487/apcyccv.v6i2.486Palabras clave:
Hipertensión Pulmonar, Defectos del Tabique Interatrial, Ecocardiografía, Ecocardiografía de ContrasteResumen
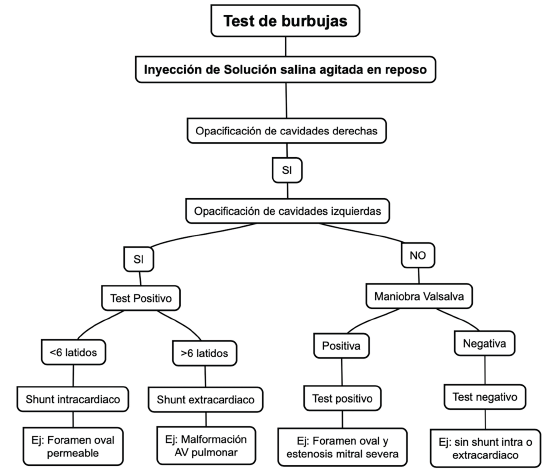
El abordaje diagnóstico de la hipertensión pulmonar mediante imágenes cardíacas, como la ecocardiografía, representa una ayuda práctica, accesible y una herramienta muy valiosa; define la probabilidad inicial diagnostica; además, brinda parámetros pronósticos y puede ayudar en el diagnóstico etiológico. La prueba de solución salina agitada, contraste con solución salina/burbujas o prueba de burbujas por ecocardiografía puede orientar no solo en el diagnóstico, sino también en la caracterización e identificación de distintas causas de hipertensión pulmonar.
Descargas
Referencias
Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RMF, Brida M, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(38):3618-731. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237.
Farber HW, Foreman AJ, Miller DP, McGoon MD. REVEAL Registry: Correlation of Right Heart Catheterization and Echocardiography in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: right heart catheterization vs echocardiography in PAH. Congest Heart Fail. 2011;17(2):56-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7133.2010.00202.x.
Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, Hua L, Handschumacher MD, Chandrasekaran K, et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: A Report from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23(7):685-713. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2010.05.010.
Cordina RL, Playford D, Lang I, Celermajer DS. State-of-the-Art Review: Echocardiography in Pulmonary Hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2019;28(9):1351-64. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2019.03.003.
Waggoner AD, Ehler D, Adams D, Moos S, Rosenbloom J, Gresser C, et al. Guidelines for the cardiac sonographer in the performance of contrast echocardiography: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council on Cardiac Sonography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2001;14(5):417-20. doi: 10.1067/mje.2001.113817.
Porter TR, Abdelmoneim S, Belcik JT, McCulloch ML, Mulvagh SL, Olson JJ, et al. Guidelines for the Cardiac Sonographer in the Performance of Contrast Echocardiography: A Focused Update from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014;27(8):797-810. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.05.011.
Mattioli A. Atrial septal aneurysm as a cardioembolic source in adult patients with stroke and normal carotid arteries. A multicentre study. Eur Heart J. 2001;22(3):261-8. oi: 10.1053/euhj.2001.2293.
Natanzon A, Goldman ME. Patent foramen ovale: Anatomy versus pathophysiology—which determines stroke risk? J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16(1):71-6. doi: 10.1067/mje.2003.34.
Marriott K, Manins V, Forshaw A, Wright J, Pascoe R. Detection of Right-to-Left Atrial Communication Using Agitated Saline Contrast Imaging: Experience with 1162 Patients and Recommendations for Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013;26(1):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2012.09.007.
Silvestry FE, Cohen MS, Armsby LB, Burkule NJ, Fleishman CE, Hijazi ZM, et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect and Patent Foramen Ovale: From the American Society of Echocardiography and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(8):910-58. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.05.015.
Soliman O, Geleijnse M, Meijboom F, Nemes A, Kamp O, Nihoyannopoulos P, et al. The use of contrast echocardiography for the detection of cardiac shunts. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2007;8(3):S2-12. doi: 10.1016/j.euje.2007.03.006.
Sharan L, Stackhouse K, Awerbach JD, Bashore TM, Krasuski RA. Effect of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(3):505-10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.04.014.
Nootens MX, Berarducci LA, Kaufmann E, Devries S, Rich S. The Prevalence and Significance of a Patent Foramen Ovale in Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest. 1993;104(6):1673-5. doi: 10.1378/ chest.104.6.1673.
Bernard S, Churchill TW, Namasivayam M, Bertrand PB. Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography in the Identification of Intra- and Extracardiac Shunts: Connecting the Dots. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2021;34(1):1-12.
Romero JR, Frey JL, Schwamm LH, Demaerschalk BM, Chaliki HP, Parikh G, et al. Cerebral Ischemic Events Associated With ‘Bubble Study’ for Identification of Right to Left Shunts. Stroke. 2009;40(7):2343-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.549683.
Jeon DS, Luo H, Iwami T, Miyamoto T, Brasch AV, Mirocha J, et al. The usefulness of a 10% air-10% blood-80% saline mixture for contrast echocardiography: Doppler measurement of pulmonary artery systolic pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(1):124-9. doi: 10.1016/ s0735-1097(01)01698-9.
Attaran RR, Ata I, Kudithipudi V, Foster L, Sorrell VL. Protocol for Optimal Detection and Exclusion of a Patent Foramen Ovale Using Transthoracic Echocardiography with Agitated Saline Microbubbles. Echocardiography. 2006;23(7):616-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1540- 8175.2006.00272.x.
Wei D, Ju Y. Importance of an Adequately Performed Valsalva Maneuver for Detecting a Right‐to‐Left Shunt Indicating Foramen Ovale Reopening. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34(5):879-83. doi: 10.7863/ ultra.34.5.879.
Montrief T, Alerhand S, Denault A, Scott J. Point-of-care echocardiography for the evaluation of right-to-left cardiopulmonary shunts: a narrative review. Can J Anesth Can Anesth. 2020;67(12):1824- 38. doi: 10.1007/s12630-020-01813-2.
Freeman JA, Woods TD. Use of Saline Contrast Echo Timing to Distinguish Intracardiac and Extracardiac Shunts: Failure of the 3‐ to 5‐Beat Rule. Echocardiography. 2008;25(10):1127-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2008.00741.x.
Deri A, English K. Echocardiographic assessment of left to right shunts: atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, patent arterial duct. Echo Res Pract. 2018;5(1):R1-16. doi: 10.1530/ERP-17-0062.
Rasalingam R, Novak E, Rifkin RD. Improved differential diagnosis of intracardiac and extracardiac shunts using acoustic intensity mapping of saline contrast studies. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;21(3):307-317. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez129.
Yang J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Yu H, Zhang H, Lan T, et al. The efficiency of a Machine learning approach based on Spatio-Temporal information in the detection of patent foramen ovale from contrast transthoracic echocardiography Images: A primary study. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023;84:104813. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104813.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 La revista es titular de la primera publicación, luego el autor dando crédito a la primera publicación.

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.

















